Microsoft last week announced that it’s temporarily disabling the MSIX ms-appinstaller protocol handler in Windows following evidence that a security vulnerability in the installer component was exploited by threat actors to deliver malware such as Emotet, TrickBot, and Bazaloader.
MSIX, based on a combination of .msi, .appx, App-V and ClickOnce installation technologies, is a universal Windows app package format that allows developers to distribute their applications for the desktop operating system and other platforms. ms-appinstaller, specifically, is designed to help users install a Windows app by simply clicking a link on a website.
But a spoofing vulnerability uncovered in Windows App Installer (CVE-2021-43890, CVSS score: 7.1) meant that it could be tricked into installing a rogue app that was never intended to be installed by the user via a malicious attachment used in phishing campaigns.
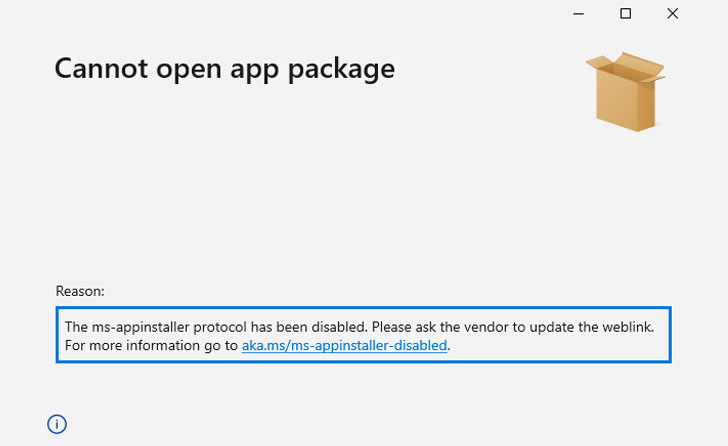
Although Microsoft released initial patches to address this flaw as part of its December 2021 Patch Tuesday updates, the company has now disabled the ms-appinstaller scheme while it works to completely plug the security hole and prevent further exploitation.
“This means that App Installer will not be able to install an app directly from a web server,” Dian Hartono said. “Instead, users will need to first download the app to their device, and then install the package with App Installer. This may increase the download size for some packages.”
With Microsoft yanking support for the protocol, the company is also recommending developers that they update the app download links on their websites by removing “ms-appinstaller:?source=” schemes so that the MSIX package or.appinstaller file can be downloaded.