Julien Gaillard, the former Chief Data Scientist at Twitter Spaces, announced on Twitter that he is leaving Silicone Valley social media giant to become Head of Data Science at DeFi lending platform Aave.
He said in that twitter’s comment that Web3’s core values are decentralization, innovation, fairness and experimentation, which encapsulates much of the feeling of the early internet.
Meanwhile, David Marcus, head of the cryptocurrency project at Facebook (now known as Meta), also started his own Web3 venture on Jan. 1.
Another Meta employee, Evan Cheng, also left in September to start MystyLab. He is currently focusing on building blockchain infrastructure and has revealed in an interview that 80% of his team’s employees come from the Web2 internet industry.
All of these prove that an era of web3 is coming to us. In this article, we will introduce web3 and the problem it solves.
The World of Web3
Web3 is a new iteration of the internet based on blockchain technology, developed with decentralization and empowerment at its core.
Whereas Web1 was a content delivery network and Web2 built out the social media ecosystem, Web3 aims to be a distributed, decentralized network.
Although the concept of Web3 is still vague, most people envision more widely distributed management and supervision rights, with members of communities and users having the ability to discuss, propose, vote on, and implement changes.
Blockchain has its origins in Bitcoin, a first major currency that does not rely on credit intermediaries, instead placing trust in a distributed, decentralized public ledger. It is a decentralized consensus mechanism free from centralized institutions.
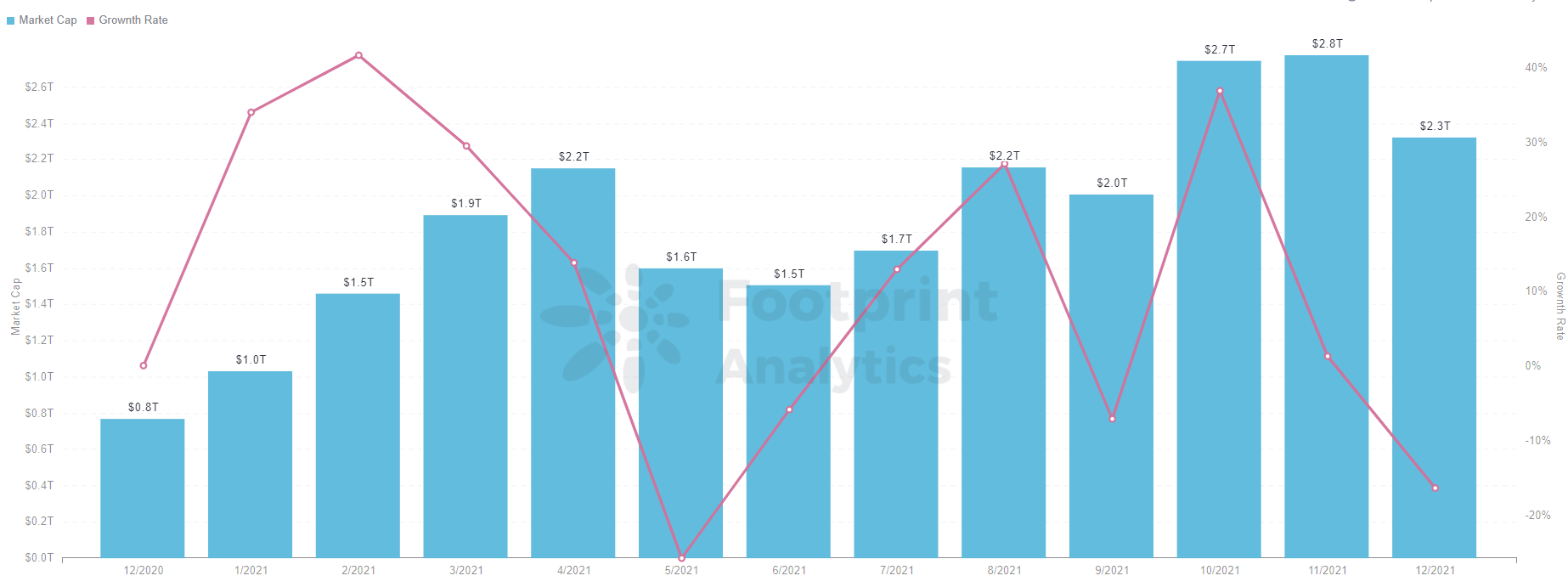
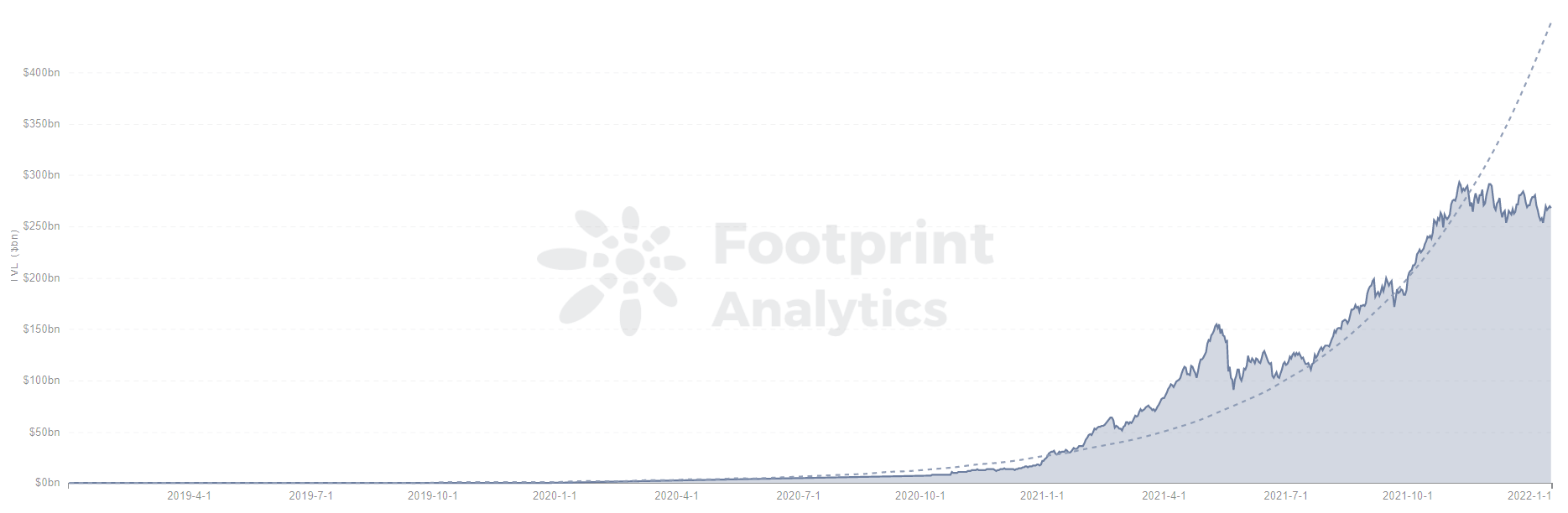
A pioneer in the application layer of blockchain technology, decentralised finance (DeFi) is an important step in the internet’s journey towards Web3. DeFi continues to dominate the application layer of blockchain technology, and Footprint Analytics has calculated the total volume locked (TVL) of decentralized finance projects over the last year, showing massive growth since 2020
Where does Web3 go next?
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAO) are widely used in blockchain, NFT and metaverse projects already. Other areas, like cloud storage, are also seeing rapid growth.
What problems does Web3 solve?
The internet is dominated by a few large internet companies, like Google, Youtube and Facebook, who use big data to recommend content. There is a growing dissatisfaction over how they handle privacy and free speech, with many desiring to escape from an ecosystem controlled by a few companies.
Problem 1: Privacy issues
Technology companies collect terabytes of user data, raising concerns about data security and personal privacy. In November 2021, a poll by the Washington Post showed that 72% of the public did not trust Facebook.
At the moment, similar data and privacy abuses are mainly addressed with government legislation, but the public’s trust in government has also diminished. A radically different model could be the solution.
In Web3, people use distributed data storage to preserve data and avoid personal data being used by centralized organizations. Projects currently working on this include decentralized storage protocol Arweave, and Secret Network, built specifically for data privacy.
Problem 2: Freedom of expression
In January 2021, Twitter blocked the account of Donald Trump for inciting violence, which also led to a worldwide discussion on freedom of expression.
At the heart of these discussions is the question of whether a social media company has the right to censor speech. But, if the era of Web3 does come, will the world have a freer online environment? It’s highly possible, with controlling rights dispersed to every connected user.
The Difficult Path to Web3
In December, Jack Dorsey, founder of Twitter and CEO of Block, tweeted that he didn’t think people could own Web3, but capital could.
Web3 needs technology and capital, and the final shape of Web3 depends heavily on the attitude of technology and capital.
Furthermore, the barriers to entry for Web3 are much higher than Web2
DeFi is more difficult to get started with than traditional finance, DeFi is more difficult to get started with than traditional finance. It is not so easy to use because it is far from fiat and our lives. It is not so easy to study because the educational system and infrastructure are not so complete.
The same is true for other areas of the blockchain application layer. It always takes time to accept completely new platforms and systems after people have adapted to centralized technology companies. The advent of the Web2 era made it possible to lower the barrier to contributing to the network. Web2 allows everyone to contribute content on the internet. Unlike the Web2 network where the barrier was low enough for everyone to join, it seems that Web3 currently needs more work from everyone in terms of barriers to entry.
What is Footprint Analytics?
Footprint Analytics is an all-in-one analysis platform to visualize blockchain data and discover insights. It cleans and integrates on-chain data so users of any experience level can quickly start researching tokens, projects and protocols. With over a thousand dashboard templates plus a drag-and-drop interface, anyone can build their own customized charts in minutes. Uncover blockchain data and invest smarter with Footprint.
CryptoSlate Newsletter
Featuring a summary of the most important daily stories in the world of crypto, DeFi, NFTs and more.
Get an edge on the cryptoasset market
Access more crypto insights and context in every article as a paid member of CryptoSlate Edge.
On-chain analysis
Price snapshots
More context


