Researchers have noticed one other malicious try by dangerous actors to breach iOS customers’ privateness. This time, they’ve found an assault state of affairs involving the iOS URL scheme. They discovered that exploiting this function may enable attackers to steal knowledge from different apps and execute different malicious actions.
iOS URL Scheme Vulnerability
In keeping with a current report from Development Micro, a brand new means of concentrating on iOS customers has surfaced on-line. They’ve allegedly discovered the misuse of Apple’s iOS URL scheme. The function that’s supposed to help apps in communication can let attackers pilfer data from different apps upon an exploit.
As defined of their blog post, Apple employs a devoted sandbox mechanism for operating each utility on iOS. This protects the customers from large damages in case of a compromise of an app because it can not influence different apps.
Nevertheless, this mechanism creates issues for purposes to work together. Thus, Apple addressed this drawback by their URL scheme function, which permits purposes to alternate data.
Whereas the function supplies comfort, there lies some drawback with it, making it weak to hijacking. When the 2 apps work together with one another through URL scheme, a malefactor can hijack it to steal knowledge. As highlighted by the researchers,
The URL Schemes operate as portals for apps to obtain data from different apps… since Apple permits totally different apps to declare the identical URL Scheme, malicious apps can hijack delicate knowledge of sure apps.
To clarify the vulnerability, they demonstrated an assault state of affairs utilizing two Chinese language apps: WeChat (messaging app), and Suning (retail utility). They defined that signing-in to Suning app through WeChat account generates a URL scheme question from Suning app to WeChat. Upon receiving the question, WeChat requests Login-Token from the server and transmits it to Suning app for verification.
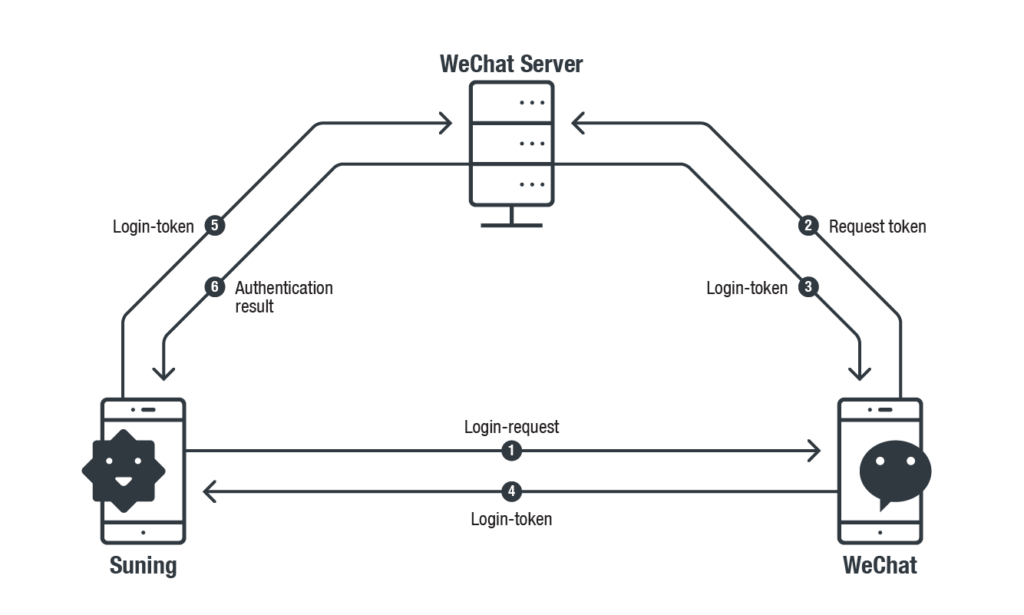
Throughout this course of, WeChat doesn’t validate the login-request supply. Whereas, Suning app makes use of the identical Login-Request URL Scheme question each time to request Login-Token from WeChat. Thus, a possible attacker can hijack this URL scheme to request a login-token from WeChat, after which use this knowledge to sign-in Suning app.
Creating Faux Apps For Assault
As defined by the researchers, profitable hijacking of a URL scheme requires the attackers to create a pretend app. For example, within the demonstrated instance, an attacker may generate a pretend WeChat app to which the Suning app would ship the login request question. That can also be fairly simple.
Capturing it from the Suning app requires creating an entire separate app with WeChat’s URL Scheme (WeChat’s URL Scheme could possibly be discovered within the subject of LSApplicationQueriesSchemesin Data.plist of Suning). With the reputable WeChat URL Scheme, a fake-WeChat could be crafted and Suning will question the pretend one for Login-Token.
Right here is how the exploit would work.
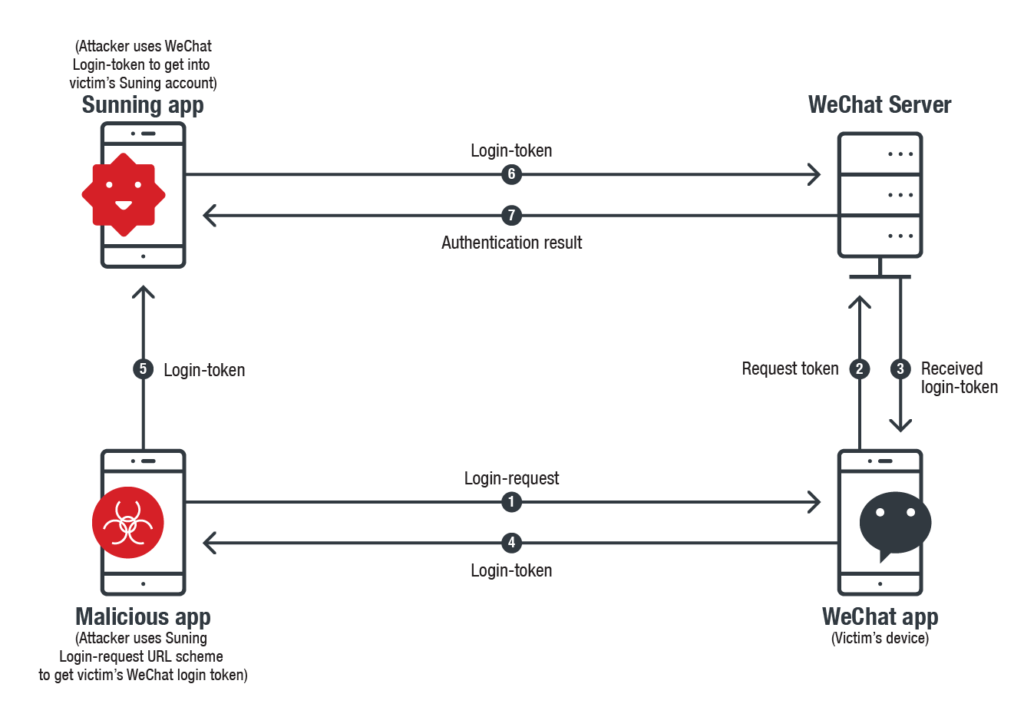
Whereas, to abuse WeChat, the identical pretend app would make use of Suning app’s distinctive URL registered with WeChat to request Login-Token. Owing to the absence of supply authentication, WeChat would merely generate the Login-Token in response to the URL.
On this means, each the apps change into uncovered to the attackers.
The attackers defined that this assault state of affairs can work with quite a few apps. They even gave one other instance the place the sufferer would pay others’ payments.
This concern shouldn’t be unique to those two apps, the vulnerability exists in lots of apps which have this specific login function.
Development Micro discovered this vulnerability in 2018 and reported the matter to the involved distributors and Apple. Apple has even notified the developers of this drawback and has really useful them utilizing Universal Links for deep linking as a substitute.
Tell us your ideas within the feedback.

