It seems the criminal hackers have a never-ending list of ways to evade security protocols and continue phishing users. Once again, researchers have spotted an innovative phishing attack going on in the wild. This time, the phishing campaign exploits Google Drive to bypass email gateways.
Phishing Campaign Exploits Google Drive
Researchers from Cofense have discovered another phishing campaign in the wild. This time, it exploits Google Drive to bypass security measures and trick users.
Since email gateways find it difficult to block legitimate services, these phishing emails easily reach users. As stated in the blog post by the researchers,
By using an authentic service, this phishing campaign was able to bypass the email security stack, in particular, Microsoft Exchange Online Protection, and make its way to the end-user.
The attack begins when the email reaches a victim’s inbox. The content of the email also contains legit Google Drive links.
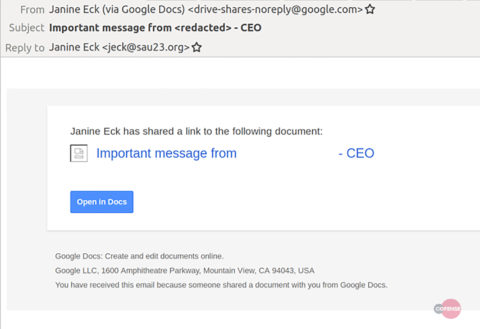
These links redirect the victim to documents that contains the actual phishing links.
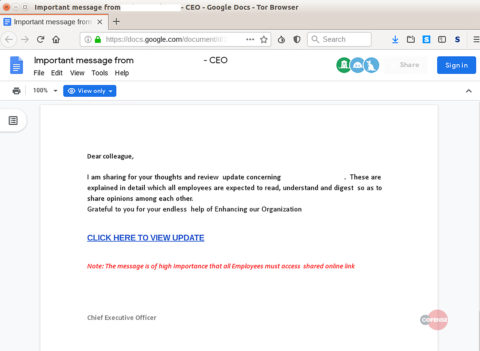
Clicking further on these links then redirects the victim to the phishing web page where, if tricked, the user would share login credentials.
Campaign Targets The Energy Sector
According to the researchers, this phishing campaign particularly targets users from the energy sector. As revealed, the phishing email’s content makes it look legit appearing from the CEO of a targeted firm. The recipients wrongly believe that the email originates from the CEO and is shared via Google Drive on his behalf.
Furthermore, the attackers have also taken care of customizing the emails according to the target firm.
The document used in this campaign was highly tailored to the targeted energy sector company. The key information used in their social engineering template included the CEO’s name, the business decision, and the company logo.
However, owing to the outdated information in the email, it became easy to detect it as a scam.
While the campaign is robust enough to evade email gateways, the researchers have shared possible mitigation. As noted, one of the malicious links in the email redirects users to a newly created phishing page. Therefore, applying a method to block new domains might help in protecting the end-user.
One automated security mechanism that might be able to defend against this part of the attack scenario is a network content filtering appliance keyed on blocking newly registered domains. This security mechanism would have stopped the end user from getting to the fake login page because of the registration date of the website.
Nonetheless, such measures can only provide partial security. The organizations must ensure developing awareness in the employees to stay wary of such attacks.
Let us know your thoughts in the comments.

